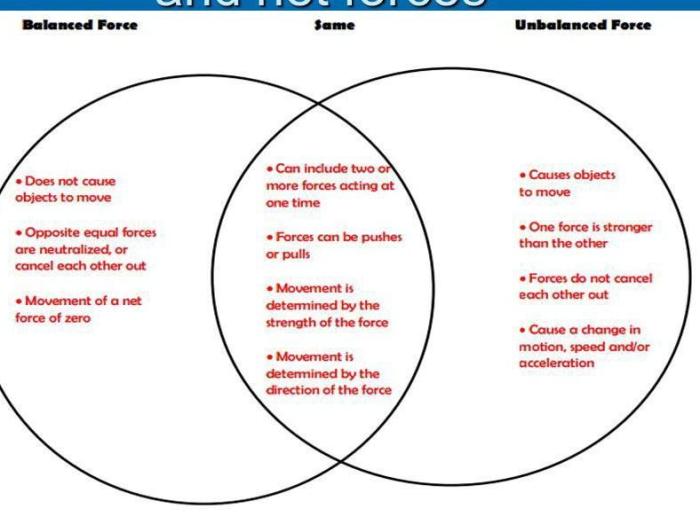
The venn diagram of balanced and unbalanced forces provides a visual representation of the similarities and differences between these two types of forces, helping us understand their impact on objects and their motion.
Balanced forces act on an object in opposite directions with equal magnitudes, resulting in no net force and no change in motion. Unbalanced forces, on the other hand, result in a net force that causes the object to accelerate in the direction of the stronger force.
Definition and Characteristics of Balanced and Unbalanced Forces: Venn Diagram Of Balanced And Unbalanced Forces
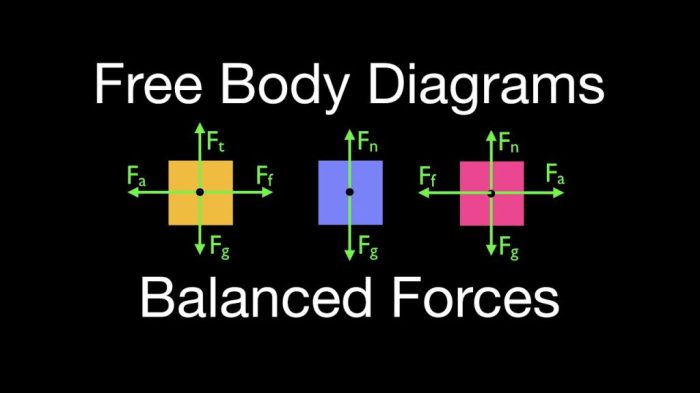
Forces are pushes or pulls that act on objects. When multiple forces act on an object, their combined effect determines the object’s motion.
Balanced forcesoccur when the net force acting on an object is zero. This means that the forces acting on the object cancel each other out. When balanced forces act on an object, the object will not accelerate and will maintain its current velocity.
Unbalanced forcesoccur when the net force acting on an object is not zero. This means that the forces acting on the object do not cancel each other out. When unbalanced forces act on an object, the object will accelerate in the direction of the net force.
Examples of balanced forces include:
- An object sitting at rest on a table
- An object moving at a constant velocity
- Two people pushing on an object with equal force in opposite directions
Examples of unbalanced forces include:
- An object falling due to gravity
- An object being pushed by a single force
- An object being pulled by a rope
Venn Diagram Representation of Balanced and Unbalanced Forces
The following Venn diagram represents the similarities and differences between balanced and unbalanced forces:
- Overlap:Both balanced and unbalanced forces can act on an object simultaneously.
- Unique to balanced forces:Balanced forces result in no acceleration of the object.
- Unique to unbalanced forces:Unbalanced forces result in acceleration of the object.
Effects of Balanced and Unbalanced Forces on Objects
Balanced forceshave no effect on an object’s velocity or direction of motion. This is because the forces acting on the object cancel each other out, resulting in a net force of zero.
Unbalanced forces, on the other hand, can cause an object to accelerate, change velocity, or change direction of motion. The magnitude and direction of the unbalanced force will determine the specific effect on the object’s motion.
For example, if an unbalanced force is applied to an object at rest, the object will accelerate in the direction of the force. If an unbalanced force is applied to an object moving at a constant velocity, the object will accelerate in the direction of the force and its velocity will change.
Applications of Balanced and Unbalanced Forces in Engineering and Physics
Engineers and physicists use balanced and unbalanced forces in a variety of applications:
- Balanced forces:Engineers use balanced forces to maintain stability and equilibrium in structures and systems. For example, the forces acting on a bridge must be balanced in order to prevent the bridge from collapsing.
- Unbalanced forces:Physicists use unbalanced forces to create motion, change momentum, and perform work. For example, a rocket engine uses unbalanced forces to propel the rocket forward.
Additional Considerations and Examples

Several factors can influence the balance or imbalance of forces acting on an object. These factors include:
- Friction:Friction is a force that opposes the motion of objects. Friction can cause balanced forces to become unbalanced, and vice versa.
- Gravity:Gravity is a force that attracts objects towards each other. Gravity can cause unbalanced forces to become balanced, and vice versa.
- Air resistance:Air resistance is a force that opposes the motion of objects through the air. Air resistance can cause unbalanced forces to become balanced, and vice versa.
Here are some additional examples of balanced and unbalanced forces in different contexts:
- Sports:When a soccer player kicks a ball, the unbalanced force of the player’s foot causes the ball to accelerate.
- Transportation:When a car is driving at a constant speed, the balanced forces of the engine’s thrust and the drag of the air keep the car moving at that speed.
- Everyday life:When you lift a book off the ground, the unbalanced force of your hand causes the book to accelerate upwards.
FAQ Explained
What is the key difference between balanced and unbalanced forces?
Balanced forces have equal magnitudes and opposite directions, resulting in no net force, while unbalanced forces have a net force that causes acceleration.
How does a venn diagram help visualize balanced and unbalanced forces?
A venn diagram shows the overlapping and unique characteristics of balanced and unbalanced forces, making it easier to compare and contrast them.