Three deadly choices vehicle and lane management – In the realm of traffic engineering, three deadly choices confront drivers as they navigate lane changes. Understanding these choices and their consequences is paramount for enhancing road safety and preventing accidents. This article delves into the fundamentals of vehicle and lane management, exploring the causes and contributing factors to poor lane change decisions, and presenting best practices and mitigation strategies to minimize risks.
The consequences of these choices can be dire, leading to accidents with severe or even fatal outcomes. Statistics and case studies underscore the significance of these decisions, highlighting the need for effective driver education and awareness campaigns.
Vehicle and Lane Management Basics: Three Deadly Choices Vehicle And Lane Management

Vehicle and lane management are essential components of traffic engineering, aiming to optimize traffic flow, enhance safety, and reduce congestion. Common techniques include lane striping, lane marking, and signal timing to guide vehicles and facilitate efficient movement.
Benefits and Limitations
- Improved traffic flow and reduced congestion
- Enhanced safety through reduced lane-changing conflicts
- Limitations: Can be complex to implement and require ongoing maintenance
Three Deadly Choices
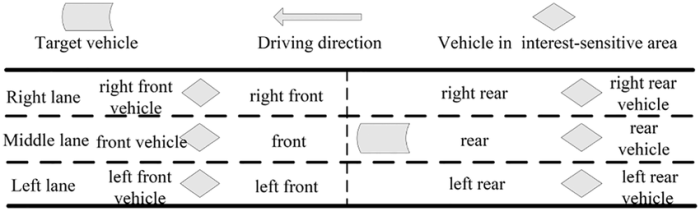
When making lane changes, drivers face three critical choices that can significantly impact safety:
Check and Clear
The driver checks their mirrors and blind spots to ensure it is clear before changing lanes.
Signal and Check
The driver signals their intention to change lanes, then checks mirrors and blind spots again before proceeding.
Check, Signal, and Check Again
The driver checks mirrors and blind spots, signals their intention, then checks mirrors and blind spots again before changing lanes.
Consequences and Statistics
Failing to make the safest choice can lead to accidents. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), lane-changing crashes account for approximately 10% of all fatal crashes in the United States.
Causes and Contributing Factors
Human Factors
- Distracted driving
- Lack of attention and awareness
- Impatience and aggressive driving
Vehicle Design
- Blind spots and limited visibility
- Poor mirror placement
- Inadequate lighting
Roadway Infrastructure
- Narrow lanes and limited sight distance
- Confusing lane markings and signage
- Poor road conditions
Best Practices and Mitigation Strategies
Safe Lane Change Maneuvers, Three deadly choices vehicle and lane management
- Use proper signaling
- Check mirrors and blind spots thoroughly
- Be aware of other vehicles and their intentions
Technology Assistance
- Lane departure warning systems
- Blind spot monitoring
- Adaptive cruise control
Innovative Lane Management Strategies
- Dedicated turning lanes
- Reversible lanes
- High-occupancy vehicle (HOV) lanes
Public Education and Awareness

Importance of Public Education
Educating drivers about the three deadly choices is crucial to improve lane change safety.
Methods for Educating Drivers
- Public service announcements
- Driver education programs
- Online resources and simulations
Evaluation of Educational Programs
Evaluating the effectiveness of educational programs is essential to identify areas for improvement and ensure their impact.
FAQ Insights
What are the three deadly choices in lane changes?
The three deadly choices are: failing to check mirrors and blind spots, failing to signal intentions, and misjudging the speed and distance of other vehicles.
How do human factors contribute to poor lane change decisions?
Human factors such as fatigue, distraction, and overconfidence can impair judgment and increase the risk of making poor lane change decisions.
What are some innovative lane management strategies to improve safety?
Innovative strategies include dedicated turning lanes, reversible lanes, and the use of technology such as lane departure warning systems and blind spot monitoring.