Intrinsic motivation reflects desires that others have, revealing a complex interplay between our inner drives and external influences. Intrinsic motivations, unlike extrinsic ones, stem from within, fueled by a genuine interest or enjoyment in the activity itself. Understanding the role of external desires in shaping intrinsic motivations is crucial for fostering motivation in various settings.
Social norms, peer pressure, and societal values can significantly influence our intrinsic motivations. We may pursue activities that align with what others expect or value, even if they do not align with our own intrinsic interests. Cultural and contextual factors also play a role, as different cultures place varying importance on intrinsic motivation.
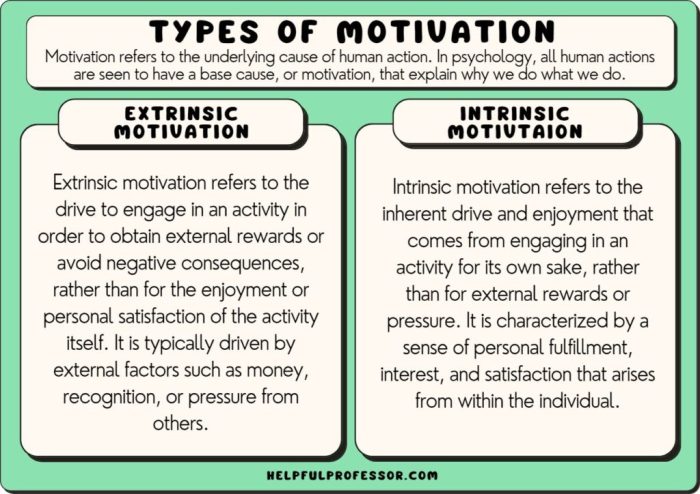
Intrinsic Motivation and its Relationship to External Desires
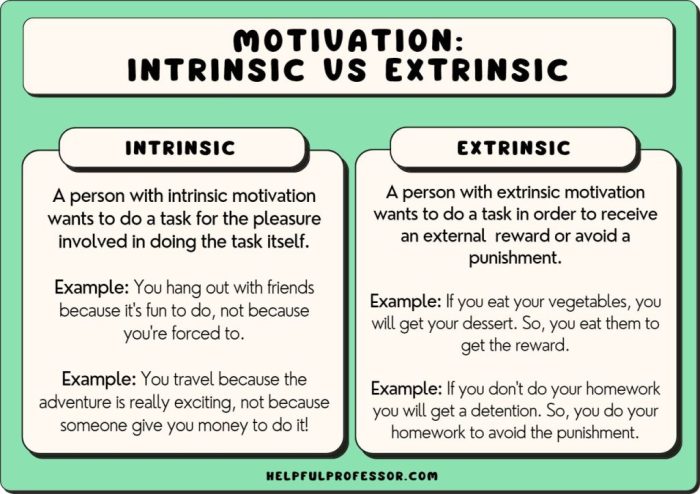
Intrinsic motivation refers to the inherent desire to engage in an activity for its own sake, driven by internal rewards and satisfaction rather than external incentives. It is characterized by:
- Autonomy: Acting out of one’s own volition and choice.
- Competence: Feeling capable and skilled in performing the activity.
- Relatedness: Experiencing a sense of connection and belonging through the activity.
Intrinsic motivations differ from extrinsic motivations, which are driven by external rewards such as grades, money, or praise. While extrinsic motivations can be effective in short-term performance, they tend to be less sustainable and can undermine intrinsic motivation over time.
External desires can shape intrinsic motivations by providing a sense of purpose or meaning to an activity. For example, a student who is passionate about science may be intrinsically motivated to study because it aligns with their desire to understand the world.
Impact of Social Influences on Intrinsic Motivation, Intrinsic motivation reflects desires that others have
Social influences play a significant role in shaping intrinsic motivations. Social norms and expectations can influence an individual’s perception of the value and importance of an activity.
- Peer pressure: Individuals may conform to the activities and behaviors of their peers, which can either enhance or diminish their intrinsic motivation.
- Societal values: Cultural values and beliefs can shape the perceived value and desirability of certain activities, influencing intrinsic motivations.
- Social comparison: Comparing oneself to others can lead to feelings of inadequacy or superiority, which can affect intrinsic motivation.
Cultural and Contextual Factors in Intrinsic Motivation
Intrinsic motivation is influenced by cultural and contextual factors. Cultural differences exist in the expression and valuation of intrinsic motivation:
- Individualistic cultures tend to emphasize personal autonomy and self-directedness, while collectivist cultures prioritize social harmony and group goals.
- Socioeconomic status, education, and other contextual factors can also shape intrinsic motivation, affecting access to resources and opportunities.
- Cultural values and beliefs influence the perception of intrinsic motivation, such as whether it is seen as a virtue or a form of selfishness.
Practical Applications of Understanding Intrinsic Motivation
Understanding intrinsic motivation has practical applications in various settings:
- Education: Fostering intrinsic motivation in students can enhance learning outcomes, engagement, and creativity.
- Workplace: Creating a work environment that supports intrinsic motivation can lead to increased productivity, job satisfaction, and employee retention.
- Well-being: Activities driven by intrinsic motivation are associated with increased well-being, personal growth, and fulfillment.
Detailed FAQs: Intrinsic Motivation Reflects Desires That Others Have
What are the key characteristics of intrinsic motivation?
Intrinsic motivation is characterized by an internal drive, enjoyment, and a sense of autonomy in the activity.
How do social influences affect intrinsic motivation?
Social norms, peer pressure, and societal values can shape our intrinsic motivations, leading us to pursue activities that align with external expectations.
What role do cultural factors play in intrinsic motivation?
Cultural values and beliefs can influence the expression and valuation of intrinsic motivation, varying across different cultures.