Protons neutrons and electrons practice worksheet answers – Delving into the realm of protons, neutrons, and electrons, this comprehensive guide unveils the fundamental building blocks of matter. With protons, neutrons, and electrons practice worksheet answers at our disposal, we embark on a captivating journey to unravel the secrets of these subatomic particles.
This guide meticulously dissects the nature, characteristics, and interactions of protons, neutrons, and electrons. By exploring their unique properties and roles within the atom, we gain a deeper understanding of the very essence of matter and its behavior.
Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
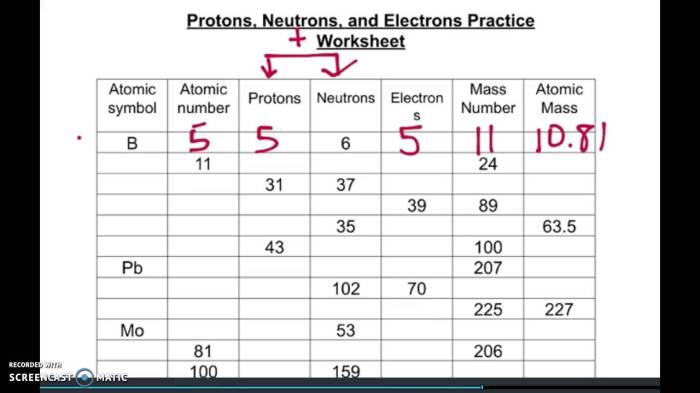
The fundamental building blocks of matter are protons, neutrons, and electrons. These subatomic particles determine the properties and behavior of atoms and molecules, forming the basis of chemistry, physics, and many other scientific disciplines.
Proton Definition and Characteristics
Protons are positively charged subatomic particles found within the nucleus of an atom. They have a mass of approximately 1 atomic mass unit (amu) and carry a charge of +1 elementary charge.
Protons play a crucial role in defining the identity of an element. The number of protons in an atom, known as the atomic number, determines its position on the periodic table and its chemical properties.
Neutron Definition and Characteristics
Neutrons are subatomic particles found within the nucleus of an atom. They have a mass of approximately 1 amu but carry no electrical charge, making them neutral.
Neutrons contribute to the mass of an atom but do not directly affect its chemical properties. They play a vital role in stabilizing the nucleus, particularly in heavier atoms.
Electron Definition and Characteristics, Protons neutrons and electrons practice worksheet answers
Electrons are negatively charged subatomic particles that orbit the nucleus of an atom. They have a mass of approximately 1/1836 amu and carry a charge of -1 elementary charge.
Electrons are responsible for the chemical bonding between atoms, forming the basis of molecular structure and interactions. They also play a crucial role in electrical and thermal conductivity.
Relationships Between Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
The number of protons and electrons in an atom must be equal to maintain electrical neutrality. The sum of the number of protons and neutrons, known as the mass number, determines the mass of an atom.
Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. Isotopes have identical chemical properties but different physical properties due to their varying masses.
Applications of Proton, Neutron, and Electron Understanding
The understanding of protons, neutrons, and electrons has revolutionized various scientific fields:
- Chemistry:Understanding electron configurations and bonding enables the prediction and analysis of chemical reactions and properties.
- Physics:The study of protons and neutrons in the nucleus has led to advancements in nuclear physics and particle accelerators.
- Medicine:The use of radioactive isotopes in medical imaging and cancer treatment relies on the principles of nuclear chemistry.
FAQ: Protons Neutrons And Electrons Practice Worksheet Answers
What is the fundamental difference between protons and electrons?
Protons possess a positive charge, while electrons carry a negative charge. Additionally, protons are located within the nucleus of an atom, whereas electrons orbit the nucleus.
How do neutrons contribute to the stability of an atom?
Neutrons, despite having no electrical charge, play a crucial role in stabilizing atomic nuclei. Their presence helps counteract the repulsive forces between positively charged protons.
What is the significance of the atomic number in an element?
The atomic number of an element represents the number of protons in its nucleus. It uniquely identifies each element and determines its position on the periodic table.